Understanding Your Path Forward
Navigating the path to parenthood can feel overwhelming, especially when exploring fertility treatment options. For many individuals and couples facing infertility, intrauterine insemination (IUI) represents a significant and hopeful first step. It is a less invasive and more affordable procedure compared to other advanced treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF), making it a common starting point for many fertility journeys. However, understanding your actual chances of success is critical to managing expectations and making informed decisions about your reproductive health.
What is Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)?
Intrauterine insemination is a fertility treatment that involves placing specially prepared sperm directly inside a woman’s uterus to facilitate fertilization. The primary goal of IUI is to increase the number of high-quality, motile sperm that reach the fallopian tubes, thereby increasing the likelihood of an egg being fertilized. By bypassing the cervix, the procedure gives the sperm a crucial head start on its journey toward the egg.
This fertility treatment works best when timing is precise and when sperm quality is adequate. The procedure itself is straightforward and carries minimal risks, making it an accessible option for many couples seeking reproductive support.
Who is IUI For? Understanding Ideal Candidates
Intrauterine insemination is often recommended for specific types of infertility. Ideal candidates include:
-
Couples with unexplained infertility
-
Cases involving mild male factor infertility, such as slightly low sperm count or reduced sperm motility (movement)
-
Women with cervical mucus issues that may hinder sperm transport
-
Women using donor sperm, including single mothers by choice and same-sex female couples
-
Women with ovulation disorders who respond well to fertility drugs
-
Couples experiencing cervical issues that affect conception
A crucial prerequisite for IUI is that the woman must have at least one open and healthy fallopian tube, as fertilization occurs naturally within the body after the procedure. This requirement distinguishes IUI from IVF, where the location of fallopian tubes is less critical.
Why “Chances” Matter More Than Just “Rates”
While clinics often quote a general success rate, your personal “chances” are what truly matter for your unique situation. IUI success rates are not a single, static number; they are a spectrum influenced by a multitude of individual factors. Your age, the specific cause of infertility, sperm quality, the number of motile sperm available after preparation, and the number of treatment cycles you undergo all combine to create a unique probability profile for your situation. Focusing on these personalized chances provides a more realistic and empowering perspective on your fertility treatment journey.
What This Guide Will Cover
This comprehensive guide will demystify IUI success rates and outcomes. We will walk through the entire IUI process, break down success rate statistics by age, explore the key factors that influence your outcome, provide a transparent look at costs, and compare IUI with In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) to help you understand the complete fertility landscape and make the best decision for your circumstances.
Understanding the IUI Process: From Consultation to Two-Week Wait
The IUI journey is a carefully orchestrated process that aligns with your natural cycle, often enhanced with medication to optimize timing and maximize the chances of a successful outcome.
Initial Fertility Assessment: Diagnosing Infertility Causes
Before beginning an IUI cycle, your fertility specialist will conduct a thorough evaluation. This typically includes:
-
Bloodwork to assess hormone levels and evaluate ovarian reserve, including anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
-
An ultrasound to examine the uterus, ovaries, and measure endometrial thickness
-
A hysterosalpingogram (HSG) to confirm that your fallopian tubes are open and patent
-
A semen analysis for the male partner to evaluate sperm count, sperm motility (movement), and morphology (shape and structure)
This diagnostic phase is crucial for determining if IUI is the right fertility treatment for you and for establishing baseline reproductive health metrics.
Ovarian Stimulation and Ovulation Induction: Preparing for Success
An IUI cycle can be performed during a natural ovulation cycle, but success rates are often significantly higher when combined with controlled ovarian stimulation. Fertility medications like Clomid (clomiphene citrate) or letrozole are commonly used to encourage the ovaries to produce one or more mature eggs. Letrozole has been shown to produce results comparable to or better than Clomid with fewer side effects and a lower risk of multiple pregnancy.
Your fertility specialist will monitor follicular development via ultrasound monitoring and blood tests measuring hormone levels. When the egg(s) are mature (typically when follicles reach 17-20mm in size), an hCG “trigger shot” (human chorionic gonadotropin) may be administered to induce ovulation within a precise window, ensuring optimal timing for the insemination procedure.
Sperm Preparation: The Critical Sperm Washing Process
On the day of the procedure, a semen sample is collected from the male partner or thawed if using frozen sperm. This sample undergoes a process called sperm washing (or sperm washing procedure). This laboratory technique separates the healthy, motile sperm from the seminal fluid, non-motile sperm, white blood cells, and other debris that could interfere with conception or cause cramping.
The sperm washing procedure typically involves:
-
Density gradient centrifugation: Separating sperm by density
-
Swim-up technique: Allowing the most active sperm to swim into culture media
-
Microfluidic separation: Using advanced microfluidic devices to isolate high-quality sperm
The result is a small, concentrated sample of the highest quality motile sperm, ready for insemination. The total progressive motile sperm count (TPMSC) after washing is a critical predictor of IUI success—counts above 5 million significantly improve pregnancy chances.
The Insemination Procedure: What to Expect
The insemination itself is a quick and relatively painless procedure, often compared to a Pap smear. You will lie on an examination table in a comfortable position. The doctor will insert a speculum into the vagina to visualize the cervix. A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is then passed through the cervix and into the uterus. The prepared sperm sample is gently injected through the catheter into the uterine cavity. The entire process typically takes only a few minutes and requires no anesthesia.
Some patients experience mild cramping during the procedure, which typically resolves quickly. You can usually resume normal activities immediately after.
The “Two-Week Wait”: What Happens After IUI
After the IUI, you will enter the “two-week wait”—the period before you can take a reliable pregnancy test. During this time, the goal is for the motile sperm to travel through the fallopian tube, fertilize the egg, and for the resulting embryo to travel back to the uterus and implant in the uterine lining.
You may be prescribed progesterone supplements (vaginal or oral) to support the uterine lining and promote a receptive environment for a potential pregnancy. This luteal support can improve implantation rates. This waiting period can be emotionally challenging, and it’s important to focus on self-care, stress management, and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits during this critical window.
IUI Success Rates: Understanding the Data
General IUI Success Rates: What the Data Shows
On average, the pregnancy rate for a single IUI cycle ranges from 10% to 20%. This figure varies significantly based on multiple factors. The success rate is heavily dependent on the patient’s age, the reason for infertility, whether fertility medications were used, and the quality of the sperm sample after preparation.
For instance, an IUI cycle using letrozole to induce ovulation induction will generally have a higher success rate than a natural cycle without medication. Similarly, couples with unexplained infertility and normal sperm quality typically see success rates in the 15-20% range, while those with mild male factor infertility may see rates around 10-15% per cycle.
Research shows that IUI success rates are approximately:
-
With fertility medications: 15-20% per cycle
-
Without medications (natural cycle): 5-10% per cycle
-
With donor sperm: Higher success in women under 35 (up to 20%), with effectiveness remaining acceptable through age 42
Cumulative Success Rates: The Impact of Multiple Cycles
Success with IUI is often a cumulative process. The chances of conception increase over several cycles, with most of the benefit occurring in the first three to four attempts. Many fertility specialists recommend a course of three to four IUI cycles before considering other options like IVF or other advanced treatment options.
Research demonstrates:
-
After 1 cycle: ~10-15% cumulative pregnancy rate
-
After 3 cycles: ~30-45% cumulative pregnancy rate for ideal candidates
-
After 6 cycles: ~60-80% cumulative rate possible for younger, healthier patients
-
Beyond 6 cycles: Diminishing returns; success rate plateaus significantly
However, data suggests that if pregnancy has not occurred after three to four well-timed, medicated cycles, the chance of success in subsequent IUI cycles diminishes significantly. At this point, couples are typically counseled to consider advanced treatment options like IVF, which offers higher pregnancy rates through different mechanisms.
Realistic Expectations: Understanding the Statistics
It is vital to maintain realistic expectations about IUI outcomes. A 15-20% success rate per cycle means that 80-85% of cycles will not result in a pregnancy. This is not a reflection of failure but rather the statistical reality of the treatment. Many factors must align perfectly for fertilization and embryo implantation to occur, and even optimal conditions do not guarantee success.
The Age Factor: How Female Age Significantly Impacts Your IUI Chances
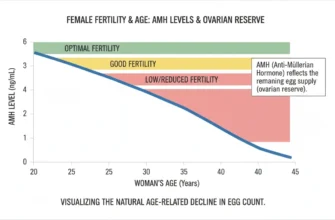
Of all the variables that influence IUI success rates, female age is the single most important predictor of treatment outcomes. This is due to the natural and progressive decline in both egg quantity and quality over time.
The Biology of Age: Understanding Ovarian Reserve and Egg Quality
A woman is born with all the eggs she will ever have—approximately 1-2 million at birth, declining to around 300,000-400,000 by menarche. As she ages, both the number of eggs (ovarian reserve, measured by anti-Müllerian hormone or AMH) and their genetic quality decline significantly.
Older eggs are more likely to have chromosomal abnormalities (aneuploidy), which can lead to:
-
Failed fertilization
-
Embryo development problems
-
Implantation failure
-
Early miscarriage
-
Ectopic pregnancy
This biological reality has a direct and profound impact on the success rate of any fertility treatment, particularly IUI, which relies on the natural quality of the egg.
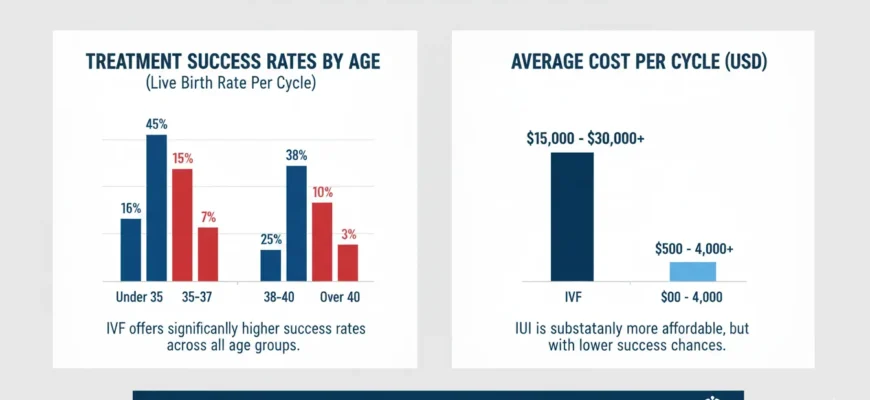
IUI Success Rates by Age Group: A Detailed Breakdown
The data clearly illustrates the impact of age on IUI pregnancy rates per cycle:
| Age Group | Success Rate Per Cycle | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Under 30 | 15-20% | Highest success; egg quality optimal; excellent response to stimulation |
| 30-34 | 12-18% | Still favorable; gradual decline in egg quality begins |
| 35-39 | 8-15% | Noticeable decline; advanced maternal age begins to impact outcomes |
| 40+ | 5% or less | Significant decline; many clinics recommend IVF as more effective option |
| Over 42 | <5% | Very low success; IVF typically recommended |
Key observations from this data:
-
Under 35: Represents optimal fertility window for IUI; egg quality is excellent and response to hormonal stimulation is typically robust
-
35-39: Success rates begin to decline noticeably as advanced maternal age effects become apparent; this age range represents a transition point for many couples
-
40 and Over: The chances decrease significantly, often falling to 5% or less per cycle. At this stage, many reproductive endocrinologists and fertility clinics may recommend moving directly to IVF, which offers higher success rates by allowing for genetic testing of embryos through preimplantation genetic testing (PGT)
Why Age is the Primary Predictor: Explaining the Biology
IUI facilitates the meeting of sperm and egg, but it cannot improve the intrinsic quality of the egg itself. Since fertilization still happens naturally inside the fallopian tube, the process is entirely dependent on having a chromosomally normal egg with adequate ovarian reserve. As a woman ages, the proportion of abnormal eggs increases dramatically due to age-related meiotic errors, making a successful pregnancy less likely with each passing year, regardless of how perfectly the IUI is timed or how much ovarian stimulation is employed.
This is why age is the most important factor in counseling patients about realistic expectations for IUI success.
Key Factors Influencing Your IUI Success (Beyond Age)
While age is paramount, several other factors play a crucial role in determining the outcome of your IUI cycles and should be carefully evaluated by your reproductive medical center.
Male Factor Infertility: The Role of Sperm Quality
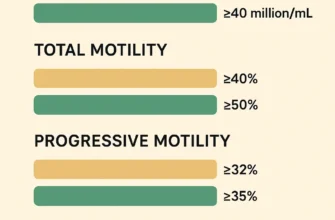
The quality of the sperm is a critical component of IUI success. Pregnancy rates are directly linked to the total progressive motile sperm count in the sample after the sperm wash. Research shows:
-
TPMSC > 5 million: Significantly improves fertilization chances
-
TPMSC ≥ 10 million: Associated with optimal outcomes
-
TPMSC < 1 million: Poor prognosis; IUI typically not recommended
A higher count of healthy, forward-moving sperm increases the probability of fertilization and pregnancy achieving success. For cases of severe male factor infertility with very low sperm count or motility, IUI is generally not effective, and IVF with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be necessary to achieve fertilization.
Other important sperm quality parameters include:
-
Sperm motility: Percentage of actively swimming sperm
-
Morphology: Percentage of normally shaped sperm (at least 4% normal forms typically required)
-
Sperm concentration: Total number of sperm per milliliter
-
Viability: Percentage of live sperm in the sample
Female Fertility Factors: Optimizing the Uterine Environment
Beyond open fallopian tubes, the health of the uterus is vital for IUI success. Key factors include:
Endometrial Thickness and Quality: A thick, receptive uterine lining is necessary for a fertilized egg to implant and grow. Research indicates:
-
Optimal range: 8-14mm, with best outcomes at 10.5-13.9mm
-
Minimum: At least 8mm recommended on the day of insemination
-
Concerning: Thickness <7mm or >14mm associated with lower pregnancy rates
Uterine Structural Issues: Conditions like uterine fibroids, polyps, scarring (adhesions), or septal deformities can interfere with embryo implantation and reduce IUI success rates significantly.
Endometrial Receptivity: Beyond thickness, the endometrium must be in the appropriate stage of development and have adequate ultrasound monitoring showing a “triple-line” pattern, indicating proper receptivity for implantation.
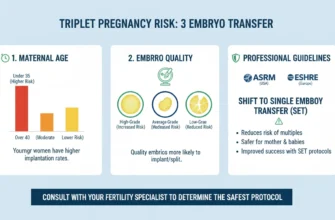
Stimulation Protocol and Response
How your body responds to fertility medications like letrozole or clomiphene matters significantly for IUI outcomes. The goal is to produce one to three mature follicles:
-
One to three follicles: Optimal; balances pregnancy chances with safety
-
More than three: Increases risk of high-order multiple pregnancies (triplets or more) and multiple gestations
-
No response: Inadequate egg development reduces chances of success
Your fertility specialist will tailor the hormonal stimulation protocol to achieve an optimal response based on your individual ovarian reserve, age, and previous response patterns. Some patients respond better to specific medication combinations or protocols, which is why individualized treatment planning is essential.
Duration of Infertility and Previous Pregnancies
The length of time a couple has been trying to conceive can impact success. Generally:
-
Longer duration of infertility: Associated with lower success rates
-
Previous pregnancy (even if not resulting in live birth): Can be a positive prognostic indicator
-
Previous live birth: Associated with better outcomes, suggesting proven fertility potential
However, these are general trends; individual circumstances vary considerably.
Unexplained Infertility: IUI as Effective First-Line Treatment
For couples with unexplained infertility, IUI combined with ovarian stimulation is often a very effective first-line treatment. This diagnosis accounts for 10-25% of infertility cases and indicates that:
-
Fallopian tubes are open and patent
-
Ovulation is occurring or can be induced
-
Sperm quality is normal or near-normal
-
No endometriosis or significant uterine abnormalities are identified
By stimulating egg production and ensuring a high concentration of sperm reaches the uterus at the optimal time, IUI helps overcome potential subtle barriers to conception that are not identified during standard female infertility diagnosis fertility testing. Success rates for unexplained infertility with IUI and ovarian stimulation are typically 15-25% per cycle—higher than the baseline rate for other diagnoses.
Additional Prognostic Factors
Research has identified several other factors affecting IUI success:
-
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) level: Higher AMH (>2.1 ng/mL) associated with better outcomes
-
Number of antral follicles: Reflects ovarian reserve
-
Body mass index (BMI): Extreme values (very low or very high) may affect outcomes
-
Endometrial pattern: Visualization on ultrasound (triple-line pattern preferred)
-
Duration since last pregnancy: Relevant for secondary infertility cases
-
Presence of pelvic infections or history of pelvic inflammatory disease: May reduce success rates
Decoding IUI Costs: A Transparent Guide to Expenses
The cost of IUI is a significant consideration for many couples. While less expensive than IVF, the expenses can accumulate over multiple cycles, and understanding the financial commitment is essential for treatment planning.
Typical Cost Breakdown for an IUI Cycle
The cost for a single IUI cycle can vary widely by location, clinic, and treatment protocol but generally falls between $500 and $4,000. This range reflects the different components that may be included:
On the lower end ($500-$1,500):
-
Basic IUI procedure only
-
Minimal monitoring
-
No fertility medications (natural cycle)
-
Limited bloodwork
On the higher end ($2,500-$4,000):
-
Monitoring ultrasounds (typically 2-4 during cycle)
-
Complete bloodwork and hormone monitoring
-
Fertility medications (Clomid, letrozole, or gonadotropins)
-
Sperm washing and preparation
-
Progesterone support during luteal phase
-
Procedure fee
-
Lab fees
Additional costs to consider:
-
Donor sperm acquisition and storage (if applicable): $500-$2,000+
-
Semen analysis and testing: $200-$500
-
Initial consultation and diagnostic testing: $300-$1,500
-
Baseline ultrasound and bloodwork: $300-$800
Medication costs are often the largest variable:
-
Oral medications (Clomid, letrozole): $30-$200 per cycle
-
Injectable gonadotropins: $3,000-$5,500 per cycle
-
Trigger shot (hCG): $30-$100
-
Progesterone support: $50-$300
Understanding Insurance Coverage: What’s Typically Covered vs. Out-of-Pocket
Insurance coverage for fertility treatment is highly variable and depends on your specific plan and state regulations:
Often covered:
-
Diagnostic testing (HSG, bloodwork, ultrasounds)
-
Some fertility medications
-
Semen analysis
Often NOT covered:
-
Fertility treatments themselves (IUI procedure)
-
Certain fertility medications
-
Sperm washing and preparation
May be covered with restrictions:
-
Limited number of cycles per year
-
Age restrictions
-
Previous treatment requirements
Critical step: Contact your insurance provider directly to understand your specific benefits, deductibles, coverage limits, and what is considered an out-of-pocket expense. Some states mandate fertility coverage, while others do not.
Potential Hidden Costs and What to Ask Your Fertility Clinic
Be sure to ask your clinic for a detailed, itemized breakdown of costs before beginning treatment. Potential expenses that may not be included in the initial quote include:
-
Bloodwork during cycle (hormone monitoring): May be per-visit charges
-
Ultrasound monitoring: Charges may be per scan
-
Prescription medications: Often need to be filled at pharmacy; check coverage
-
Progesterone supplements: Vaginal suppositories or injections
-
Cryopreservation (if freezing sperm): $300-$1,000+ per year storage
-
Additional consultation fees: If complications arise or additional monitoring needed
-
Cancellation fees: If cycle is cancelled due to poor response
-
Procedure cancellation: If another procedure (like hysteroscopy) is needed
Clarity upfront can prevent financial surprises down the road and help you budget appropriately for multiple cycles if needed.
IUI vs. IVF: Understanding Your Options
Understanding how IUI compares to in vitro fertilization (IVF) is essential for making an informed decision about your fertility treatment path.
Success Rates: IUI vs. IVF Comparison
Per-Cycle Success Rates:
| Age Group | IUI Success Rate | IVF Success Rate | Live Birth Rate (IVF) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 35 | 15-20% | 35-50% | ~50% |
| 35-37 | 10-15% | 25-40% | ~36% |
| 38-40 | 8-10% | 15-25% | ~23% |
| Over 40 | <5% | 5-15% | ~8% |
Key observations:
-
IVF offers significantly higher success rates across all age groups
-
The advantage of IVF over IUI is most pronounced in women over 35 and in cases of severe male factor infertility
-
However, for couples with unexplained infertility and normal parameters, IUI may achieve similar cumulative rates over 3-4 cycles
Cost Comparison
| Factor | IUI | IVF |
|---|---|---|
| Cost per cycle | $500-$4,000 | $12,000-$20,000+ |
| Medications | $0-$5,500 | $3,000-$8,000 |
| Total estimated for 3 cycles | $3,000-$12,000 | $36,000-$60,000+ |
| Insurance coverage | Often limited | May be mandated in some states |
| Cost per live birth | Often lower due to cumulative effect | Higher initial cost, but fewer cycles needed |
Procedure Complexity and Time Commitment
IUI:
-
Minimally invasive
-
Shorter procedure (minutes)
-
Fewer appointments
-
Can align with natural cycle
-
Typically 1-2 week process
IVF:
-
More invasive (egg retrieval required)
-
Complex procedure (10-15 minutes for retrieval)
-
Multiple monitoring appointments
-
Requires controlled ovarian stimulation
-
Typically 3-4 week process
-
Requires anesthesia for egg retrieval
When to Consider Transitioning to IVF
Fertility specialists typically recommend considering IVF after:
-
3-6 failed IUI cycles (especially if using ovarian stimulation)
-
Age over 35 with diminished success in early IUI cycles
-
Female age over 40: Many recommend starting with IVF given lower IUI success
-
Severe male factor infertility: ICSI-IVF more appropriate
-
Tubal factor infertility: IVF bypasses tubal issues
-
Low ovarian reserve: IVF allows PGT for chromosomal screening
-
Repeated IUI miscarriages: IVF with PGT may identify chromosomal issues
-
Secondary infertility with advanced maternal age: IVF more efficient
The Role of a Reproductive Endocrinologist
A reproductive endocrinologist (reproductive specialist with additional training in hormones and infertility) can help you navigate the choice between IUI and IVF based on your individual diagnosis, age, ovarian reserve, sperm parameters, and other factors affecting reproductive health.
Lifestyle Factors: Optimizing Your Chances
While not the primary determinants of IUI success, certain lifestyle modifications may support optimal outcomes:
-
Stress management: Chronic stress may impact hormonal changes affecting ovulation and implantation
-
Caffeine intake: Excessive caffeine may be associated with reduced fertility; moderation recommended
-
Smoking and alcohol: Detrimental to sperm and egg quality; cessation recommended
-
Exercise: Moderate activity beneficial; excessive exercise may impair ovulation
-
Nutrition: Balanced diet supporting reproductive health
-
Weight management: Extreme values may reduce fertility; maintain healthy BMI
-
Sleep: Adequate sleep supports hormonal regulation
-
Preconception counseling: Consider discussing with your fertility specialist
Your Path Forward
Intrauterine insemination is a valuable and effective fertility treatment for many individuals and couples, offering a less invasive path toward building a family. Success is not just a single number but a complex interplay of factors, with female age being the most significant determinant of your chances. The quality of motile sperm, the health of the uterine environment (reflected in endometrial thickness and ultrasound findings), and the response to ovarian stimulation also play critical roles.
Your fertility journey is unique, and understanding the complete picture—from the IUI procedure and success rates to associated costs and cumulative pregnancy rates—empowers you to set realistic expectations. While pregnancy rate statistics per cycle are modest, the cumulative effect of several well-planned cycles provides a legitimate opportunity for conception for the right candidates.
The most crucial next step is to have an open and thorough discussion with a fertility specialist or reproductive endocrinologist. They can assess your individual circumstances, provide a personalized prognosis based on your age, ovarian reserve, sperm quality, and other relevant factors, and help you decide if intrauterine insemination is the right starting point for you, or if another treatment like IVF might offer a more direct route to success given your specific diagnosis.
Armed with comprehensive knowledge about artificial insemination, realistic expectations, and guidance from experienced fertility professionals, you can navigate your fertility journey with confidence and clarity—taking one informed step at a time toward your goal of parenthood.